
In the cells of the medulla we find chromaffin and argentaffin granules, containing mainly catecholamines.

The medulla originates from the neural crest, and therefore its cells can be thought of as modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons. The adrenal medulla consists of irregularly shaped trabeculae between which the capillary sinusoids pass. The secretory granules of this layer contain mainly androgens and, to a minor extent, glucocorticoids.
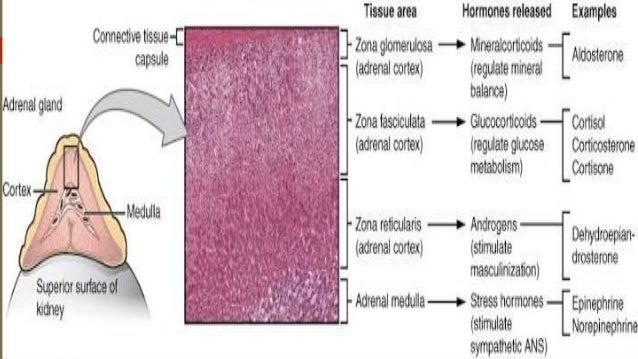
The cells are smaller compared to the previous layers, in some of them we find a nucleus of irregular shape, the cytoplasm contains a large amount of lipofuscin. Zona reticularis is composed of cells that are arranged in irregularly anastomosing trabeculae.They produce glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, and small amounts of androgens. The cells are polyhedral in shape and contain a large number of lipid droplets in the cytoplasm. Zona fasciculata occupies 65% of the volume of the adrenal cortex and consists of radially running trabeculae of cells.The cells produce mineralocorticoids, especially aldosterone. The cells are cylindrical or pyramidal cells and form arcuate, club-like rays that are surrounded by numerous capillaries. Zona glomerulosa is located just beneath the connective tissue capsule.The individual layers are called the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. According to the arrangement of the trabeculae, the adrenal cortex is divided into three concentric layers, which in man are not precisely delimited. The cells of the adrenal cortex do not accumulate secretory products in granules. The cells of the adrenal cortex have the characteristics of steroid-secreting cells they have a spherical, centrally placed nucleus, in the cytoplasm we can find a massively developed smooth endoplasmic reticulum, numerous mitochondria of tubular type and lipid droplets. The cells here are arranged in trabeculae surrounded by blood sinusoids. Schematic of cellular organization in the adrenal gland From this sheath, a septa containing weak arteries lead into the gland.
The gland is embedded in a connective sheath (capsula fibrosa) that sits firmly against the organ surface. The right adrenal gland is triangular in shape, the left is crescentic. On the gland we recognize the facies anterior, facies posterior and facies renalis (renal surface). Dorsally the adrenal glands insist on the diaphragm, ventrally the liver is in front of the right adrenal gland and the pancreas and stomach in front of the left.

Due to the lower position of the right kidney, the right adrenal gland is also located lower. The adrenal glands are located retroperitoneally at the upper poles of the kidneys at the level of Th11.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
